CRM Software HIPAA Compliant: Navigating the complex world of healthcare data management requires robust systems that prioritize patient privacy and security. This guide delves into the essential aspects of ensuring your CRM software meets the stringent requirements of the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA), offering practical advice and insights for healthcare organizations. Understanding HIPAA compliance isn’t just about avoiding penalties; it’s about upholding ethical responsibilities and maintaining patient trust.
We’ll explore the key HIPAA regulations relevant to CRM software, outlining the specific data elements needing protection and detailing the potential consequences of non-compliance. We’ll then examine the critical features of HIPAA-compliant CRM software, focusing on encryption, access controls, audit trails, and authentication methods. The selection and implementation process will be carefully dissected, including vendor risk assessments and data migration strategies.
Finally, we’ll address ongoing maintenance, data security best practices, and incident response planning to ensure long-term HIPAA compliance.
HIPAA Compliance Requirements for CRM Software
Implementing a Customer Relationship Management (CRM) system in a healthcare setting requires careful consideration of the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act of 1996 (HIPAA). Failure to comply with HIPAA regulations can result in significant financial penalties and reputational damage. This section details the key requirements and considerations for ensuring your CRM system operates within the bounds of HIPAA compliance.
Core HIPAA Regulations Relevant to CRM Software
HIPAA’s Privacy Rule and Security Rule are the most pertinent regulations for CRM systems used in healthcare. The Privacy Rule protects the privacy of individually identifiable health information (IIHI), while the Security Rule establishes national standards for the security of electronic protected health information (ePHI). These rules dictate how protected health information must be handled, stored, transmitted, and accessed.
Specifically, CRM systems must adhere to requirements related to access controls, data integrity, audit trails, and the implementation of appropriate safeguards against unauthorized access, use, disclosure, alteration, or destruction of ePHI.
Protected Data Elements Handled by CRM Systems
CRM systems in healthcare environments often store a wide range of sensitive data elements considered ePHI under HIPAA. This includes patient names, addresses, dates of birth, medical record numbers, diagnoses, treatment information, insurance details, and communication logs related to healthcare services. Even seemingly innocuous data, when combined, can be used to identify an individual, making it crucial to treat all data within the CRM system as potentially sensitive.
For example, a seemingly harmless combination of a patient’s name and date of birth could lead to the identification of their medical record.
Examples of HIPAA Violations Related to CRM Software
Non-compliant CRM software can lead to several HIPAA violations. For example, a system lacking robust access controls might allow unauthorized personnel to view patient records, breaching the Privacy Rule. A system failing to encrypt ePHI during transmission could expose it to interception, violating the Security Rule. Similarly, inadequate security measures such as weak passwords or a lack of regular security updates could allow hackers to access the system and steal sensitive patient data.
A lack of a comprehensive audit trail could hinder investigations into potential data breaches, hindering compliance efforts. Failing to implement appropriate administrative, physical, and technical safeguards as Artikeld by HIPAA could also result in significant violations.
Checklist for Evaluating HIPAA Compliance of a CRM System
Before implementing a CRM system, a thorough evaluation of its HIPAA compliance is essential. The following checklist provides key areas to assess:
- Access Controls: Does the system enforce role-based access controls, limiting access to ePHI based on individual roles and responsibilities?
- Data Encryption: Does the system encrypt ePHI both at rest and in transit?
- Audit Trails: Does the system maintain comprehensive audit trails of all access and modifications to ePHI?
- Security Updates: Does the vendor provide regular security updates and patches to address vulnerabilities?
- Business Associate Agreements (BAAs): If using a third-party CRM vendor, is a valid BAA in place that Artikels their HIPAA compliance responsibilities?
- Data Backup and Disaster Recovery: Does the system have robust backup and disaster recovery procedures to ensure data availability and integrity in case of a system failure or disaster?
- Employee Training: Does the organization provide comprehensive HIPAA training to all employees who have access to the CRM system?
- Risk Assessment: Has a thorough risk assessment been conducted to identify and mitigate potential security risks associated with the CRM system?
Features of HIPAA-Compliant CRM Software
HIPAA-compliant CRM software goes beyond the capabilities of standard CRM systems by incorporating robust security measures designed to protect sensitive patient data. These features are crucial for healthcare organizations to maintain compliance with the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA). The key differentiators lie in the level of data protection, access control, and auditability offered.
The core functionality of a standard CRM—managing contacts, tracking interactions, and streamlining workflows—remains, but the HIPAA-compliant version significantly enhances these features with a focus on data security and privacy. This ensures that protected health information (PHI) remains confidential, available only to authorized personnel, and protected from unauthorized access, use, disclosure, disruption, modification, or destruction.
Encryption and Access Controls
Encryption and access controls are fundamental to HIPAA compliance. Data encryption, both in transit (while data is being transmitted) and at rest (while data is stored), safeguards PHI from unauthorized access even if a security breach occurs. Strong encryption algorithms, such as AES-256, are essential. Access controls restrict access to PHI based on the principle of least privilege; users are granted only the access necessary to perform their job duties.
Role-based access control (RBAC) is a common implementation, assigning different permission levels to various user roles within the organization. For example, a receptionist might only have access to scheduling information, while a physician might have access to complete patient records. This granular control prevents unauthorized personnel from viewing or modifying sensitive information.
Audit Trails and Logging Mechanisms
Comprehensive audit trails and logging mechanisms are critical for demonstrating compliance. These features record all actions performed within the CRM system, including user logins, data access, modifications, and deletions. This detailed record provides a verifiable history of all activities, allowing for the identification of potential security breaches or unauthorized access attempts. A robust audit trail should include timestamps, user IDs, and a description of the action performed.
For example, a log entry might indicate that Dr. Smith accessed John Doe’s medical records at 2:15 PM on October 26th. Regular review of these logs is essential for identifying and addressing potential security issues.
Authentication Methods
HIPAA-compliant CRM systems employ strong authentication methods to verify user identities before granting access. Multi-factor authentication (MFA), which requires users to provide multiple forms of authentication (e.g., password and a one-time code from a mobile app), is highly recommended. Other methods include strong password policies, biometric authentication (fingerprint or facial recognition), and single sign-on (SSO) integration with existing organizational security systems.
The selection of authentication methods should be based on a risk assessment, considering the sensitivity of the data being protected and the potential threats. For instance, a hospital might use MFA for all staff accessing patient records, while a smaller clinic might use a combination of strong passwords and SSO.
Selecting and Implementing HIPAA-Compliant CRM Software
Choosing and implementing HIPAA-compliant CRM software requires careful planning and execution to ensure patient data remains protected. This process involves a thorough assessment of organizational needs, vendor evaluation, and a robust data migration strategy. Failure to properly address these steps can lead to significant compliance risks and potential legal repercussions.
Step-by-Step Guide for Selecting HIPAA-Compliant CRM Software
Selecting the right HIPAA-compliant CRM involves a systematic approach. A rushed decision can compromise security and functionality. The following steps provide a structured framework for this crucial process.
- Define Requirements: Clearly articulate your organization’s specific needs. Consider factors such as the number of users, data storage requirements, desired functionalities (e.g., appointment scheduling, patient communication), and integration with existing systems.
- Identify Potential Vendors: Research and create a shortlist of vendors offering HIPAA-compliant CRM solutions. Look for vendors with a strong track record of compliance and robust security measures.
- Request Demonstrations and Consultations: Schedule demonstrations with your shortlisted vendors to assess the software’s usability and features. Ask detailed questions about their security protocols, compliance certifications, and data breach response plans.
- Compare Vendor Offerings: Evaluate the vendors based on your defined requirements, considering factors like cost, scalability, ease of use, and technical support.
- Negotiate Contracts: Carefully review the contract terms and conditions, ensuring that they align with your organization’s needs and comply with HIPAA regulations. Pay close attention to data ownership, security responsibilities, and breach notification procedures.
- Implementation Planning: Develop a detailed implementation plan that includes timelines, resource allocation, and training for staff. Consider a phased rollout to minimize disruption to ongoing operations.
Comparison of Vendor Offerings
A direct comparison of vendors helps in making an informed decision. The following table illustrates a sample comparison; actual vendors and features will vary.
| Vendor | Key Features | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| Vendor A | Secure messaging, appointment scheduling, patient portal integration | Robust security features, excellent customer support | Higher cost, steeper learning curve |
| Vendor B | Contact management, task management, reporting and analytics | User-friendly interface, affordable pricing | Limited integration options, fewer security features compared to Vendor A |
| Vendor C | Comprehensive patient data management, customizable workflows | Highly scalable, strong security certifications | Complex configuration, requires specialized IT expertise |
Vendor Risk Assessment
A thorough vendor risk assessment is critical before implementation. This process helps identify and mitigate potential security risks associated with the chosen vendor.
- Security Policies and Procedures: Review the vendor’s security policies and procedures to ensure they align with HIPAA requirements. This includes their physical security measures, access controls, data encryption methods, and business associate agreements (BAAs).
- Compliance Certifications: Verify the vendor’s compliance certifications, such as SOC 2, ISO 27001, or HITRUST CSF. These certifications demonstrate a commitment to security and compliance.
- Data Breach Response Plan: Evaluate the vendor’s data breach response plan to ensure it’s comprehensive and addresses notification procedures, remediation strategies, and forensic investigation.
- Third-Party Risk Assessment: Assess the vendor’s third-party relationships to understand potential risks associated with their subcontractors or partners.
Data Migration Procedures
Migrating data to a new HIPAA-compliant CRM requires a well-defined plan to ensure data integrity and compliance.
- Data Mapping and Cleansing: Before migration, map your existing data to the new system’s fields and cleanse the data to remove duplicates and inconsistencies. This ensures accurate data transfer and reduces errors.
- Data Encryption: Encrypt all data during the migration process to protect it from unauthorized access. This is crucial for maintaining HIPAA compliance throughout the transition.
- Data Validation: After migration, validate the data in the new system to ensure accuracy and completeness. Compare the data in the old and new systems to identify any discrepancies.
- Auditing and Monitoring: Implement robust auditing and monitoring procedures to track data access and changes throughout the migration process. This provides an audit trail for compliance purposes.
Maintaining HIPAA Compliance with CRM Software
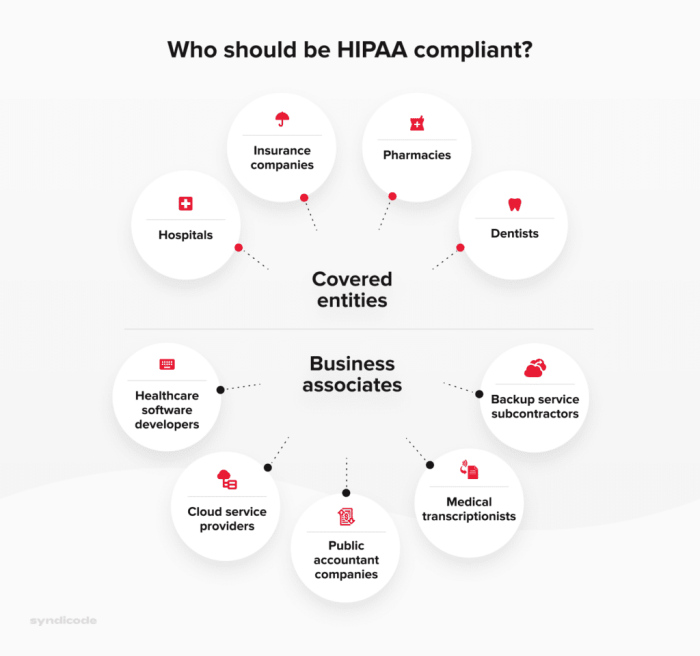
Source: syndicode.com
Maintaining HIPAA compliance for CRM software isn’t a one-time task; it’s an ongoing commitment requiring diligent effort and proactive measures. Failure to maintain compliance can lead to significant penalties and reputational damage. This section Artikels crucial aspects of ongoing maintenance to ensure the continued protection of protected health information (PHI).
Regular Security Audits and Vulnerability Assessments
Regular security audits and vulnerability assessments are critical for identifying and mitigating potential risks to PHI stored within the CRM system. These assessments should be conducted at least annually, or more frequently depending on the complexity of the system and the volume of PHI handled. Audits should encompass a review of access controls, data encryption methods, and the overall security posture of the system.
Vulnerability assessments, often performed using automated scanning tools, identify weaknesses in the system’s software and infrastructure that could be exploited by malicious actors. For example, a penetration test might simulate a cyberattack to uncover vulnerabilities in the system’s defenses. A comprehensive report detailing findings and recommended remediation steps should be generated after each assessment. Following the recommendations from these assessments is vital for maintaining compliance.
Employee Training Protocols for HIPAA Compliance, Crm software hipaa compliant
Effective employee training is paramount for ensuring HIPAA compliance. Training should be comprehensive, covering all aspects of HIPAA regulations relevant to the use of the CRM system. This includes training on proper access controls, data handling procedures, and the importance of protecting PHI. Training should be delivered regularly, ideally annually, with refresher courses conducted as needed to address new regulations or changes in the CRM system.
The training should be documented, with employees acknowledging their understanding and commitment to HIPAA compliance. Interactive modules, simulations, and regular quizzes can enhance knowledge retention and ensure employee understanding of critical procedures. For instance, employees might participate in a mock phishing exercise to learn how to identify and report suspicious emails.
Data Breach Response Plan
A well-defined data breach response plan is crucial for minimizing the impact of a HIPAA violation. This plan should Artikel procedures for detecting, containing, and reporting a breach. It should detail the steps to be taken in the event of unauthorized access, use, disclosure, alteration, or destruction of PHI. The plan should include procedures for notifying affected individuals, the Department of Health and Human Services (HHS), and other relevant parties as required by HIPAA regulations.
Choosing HIPAA-compliant CRM software is crucial for businesses handling sensitive patient data. However, the need for robust CRM extends beyond healthcare; for instance, HVAC companies benefit greatly from using specialized systems like those detailed at crm software for hvac companies. Ultimately, the selection of appropriate, compliant CRM software hinges on the specific needs and data security requirements of the individual business, regardless of industry.
The plan should also Artikel procedures for conducting a thorough investigation to determine the cause of the breach and to implement corrective actions to prevent future incidents. For example, a breach response plan might include a detailed checklist outlining the steps to take upon discovery of a breach, such as isolating affected systems, contacting law enforcement, and initiating the notification process.
Regular testing and updates of the plan are crucial to ensure its effectiveness.
Data Security Best Practices for HIPAA-Compliant CRM Systems
Source: kohezion.com
Maintaining robust data security is paramount for any HIPAA-compliant CRM system. Protecting sensitive patient information requires a multi-layered approach encompassing technical safeguards, administrative controls, and physical security measures. This section details essential best practices to ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of protected health information (PHI) within your CRM.Data security in a HIPAA-compliant CRM isn’t a one-time task; it’s an ongoing process demanding vigilance and proactive measures.
Regular audits, employee training, and the implementation of cutting-edge security technologies are crucial for staying ahead of evolving threats. Failing to implement and maintain these best practices can lead to significant legal and financial repercussions, including hefty fines and reputational damage.
Regular Software Updates and Patching
Promptly applying software updates and security patches is fundamental to mitigating vulnerabilities. Outdated software often contains known security flaws that cybercriminals actively exploit. These updates frequently include critical security fixes, addressing potential entry points for unauthorized access and data breaches. A scheduled update process, integrated into your IT maintenance routine, ensures that your CRM remains protected against the latest threats.
For example, failing to update a CRM system’s antivirus software could leave it vulnerable to malware attacks, potentially compromising sensitive patient data.
Preventing Unauthorized Access and Data Loss
Preventing unauthorized access and data loss necessitates a combination of technical and administrative controls. Strong passwords, multi-factor authentication (MFA), and access control lists (ACLs) are essential for limiting access to authorized personnel only. Data encryption, both in transit and at rest, protects PHI from unauthorized viewing even if a breach occurs. Regular data backups, stored securely offsite, provide a recovery mechanism in case of data loss due to hardware failure, natural disasters, or malicious attacks.
For instance, implementing MFA adds an extra layer of security, requiring users to provide a second form of authentication beyond their password, significantly reducing the risk of unauthorized logins. Regular data backups to a cloud-based storage system that is also HIPAA compliant can ensure business continuity in the event of a data loss incident.
Managing User Access Rights and Permissions
Effective management of user access rights and permissions is crucial for maintaining data security and complying with HIPAA regulations. This involves implementing the principle of least privilege, granting users only the access necessary to perform their job functions. Regularly reviewing and updating user access rights ensures that permissions remain appropriate and that terminated employees’ access is revoked promptly.
- Implement the principle of least privilege: Grant users only the minimum necessary access to perform their duties.
- Utilize role-based access control (RBAC): Assign users to roles with predefined permissions, simplifying access management.
- Regularly audit user access: Conduct periodic reviews of user access rights to identify and rectify any discrepancies or outdated permissions.
- Promptly revoke access for terminated employees: Ensure immediate removal of access upon employee termination to prevent unauthorized access.
- Implement strong password policies: Enforce complex passwords and regular password changes to enhance security.
- Utilize multi-factor authentication (MFA): Add an extra layer of security by requiring multiple forms of authentication for login.
Illustrative Examples of HIPAA Violations in CRM Systems
Understanding potential HIPAA violations within CRM systems is crucial for healthcare organizations to ensure patient data privacy and security. Failing to adequately protect this sensitive information can lead to severe consequences. This section provides a hypothetical scenario illustrating a potential violation and its repercussions.
Healthcare organizations must understand the risks inherent in using CRM systems to manage patient information. Even with HIPAA-compliant software, human error or inadequate security protocols can compromise protected health information (PHI).
Hypothetical HIPAA Violation Scenario
A fictional medical practice, “HealthyLife Clinic,” uses a CRM system to manage patient appointments, medical history notes, and billing information. A disgruntled employee, before their termination, downloads a significant portion of the CRM database onto a personal USB drive. This data includes patient names, addresses, diagnoses, and treatment details. The employee then shares this information with a competitor, potentially violating several HIPAA regulations, including the Privacy Rule and Security Rule.
Consequences of the HIPAA Violation
The consequences for HealthyLife Clinic would be substantial. They face potential financial penalties from the Office for Civil Rights (OCR), which could range from thousands to millions of dollars depending on the severity of the violation and the number of patients affected. Furthermore, the clinic would likely experience significant reputational damage, leading to a loss of patient trust and potential legal action from affected patients.
The OCR investigation could result in a Corrective Action Plan (CAP), requiring the clinic to implement significant changes to their data security practices and potentially leading to a costly audit. Negative media coverage could further amplify the damage, making it harder to attract new patients and retain existing ones.
Mitigation Strategies for Preventing Similar Violations
To mitigate the risk of similar violations, HealthyLife Clinic (and other healthcare organizations) should implement robust security measures. These include:
Implementing strong access controls with unique usernames and strong, regularly changed passwords for each employee. Regular security awareness training for all employees to highlight the importance of HIPAA compliance and the potential consequences of violations. Data encryption both in transit and at rest to protect data even if a breach occurs. Regular security audits and penetration testing to identify vulnerabilities and ensure the effectiveness of security measures.
Implementing a robust data loss prevention (DLP) system to monitor and prevent sensitive data from leaving the organization’s network without authorization. Maintaining detailed audit trails to track all access and modifications to patient data. Having a comprehensive incident response plan in place to handle data breaches effectively and minimize damage. Regularly reviewing and updating security policies and procedures to adapt to evolving threats and best practices.
Using multi-factor authentication (MFA) to add an extra layer of security to user logins. Conducting background checks on employees before granting access to sensitive patient data.
Closing Notes: Crm Software Hipaa Compliant
Source: jotform.com
Implementing and maintaining HIPAA-compliant CRM software is a continuous journey, not a destination. By understanding the intricacies of HIPAA regulations, carefully selecting a compliant system, and diligently adhering to best practices for data security and ongoing maintenance, healthcare organizations can effectively manage patient data while safeguarding patient privacy and upholding their ethical obligations. Proactive risk management and a commitment to continuous improvement are paramount in this critical area.
The investment in robust, compliant CRM systems ultimately translates to enhanced patient care, strengthened reputation, and minimized legal risks.
Essential Questionnaire
What specific data elements are protected under HIPAA within a CRM system?
Protected Health Information (PHI) including names, addresses, dates of birth, medical records, insurance information, and any other individually identifiable health data processed within the CRM.
How often should security audits and vulnerability assessments be conducted?
Regularly, at least annually, and more frequently depending on the system’s complexity and risk level. Consider external penetration testing as well.
What are the penalties for HIPAA violations related to CRM software?
Penalties vary widely depending on the severity and intent of the violation, ranging from significant financial fines to legal action and reputational damage.
Can a standard CRM be made HIPAA compliant through add-ons or configurations?
While some add-ons might enhance security, it’s generally safer and more reliable to choose a CRM system specifically designed and certified as HIPAA compliant from the outset.
What is Business Associate Agreement (BAA) and why is it important?
A BAA is a contract between a covered entity (healthcare provider) and a business associate (like a CRM vendor) that Artikels responsibilities for protecting PHI. It’s crucial for ensuring legal compliance.
